Are business assets inventory? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of business assets inventory, exploring its definition, components, uses, best practices, and real-world examples. By understanding the ins and outs of asset inventory management, businesses can optimize their operations, make informed decisions, and maximize their return on investment.
An accurate and up-to-date inventory of business assets is crucial for effective financial reporting, asset management, and strategic planning. It provides a clear picture of a company’s resources, helping businesses track their assets, assess their value, and make informed decisions about their use and allocation.
Definition of Business Assets Inventory

A business assets inventory is a comprehensive list of all the assets owned by a company. These assets can include physical assets, such as property, plant, and equipment, as well as intangible assets, such as intellectual property and goodwill.
Maintaining an accurate inventory of business assets is important for a number of reasons. First, it helps companies to track their assets and ensure that they are being used efficiently. Second, it helps companies to identify and manage risks associated with their assets.
Third, it helps companies to comply with accounting and financial reporting requirements.
Importance of Maintaining an Accurate Inventory
There are a number of benefits to maintaining an accurate inventory of business assets. These benefits include:
- Improved asset management
- Reduced risk of asset loss
- Improved financial reporting
- Enhanced compliance with accounting and financial reporting requirements
Components of a Business Assets Inventory
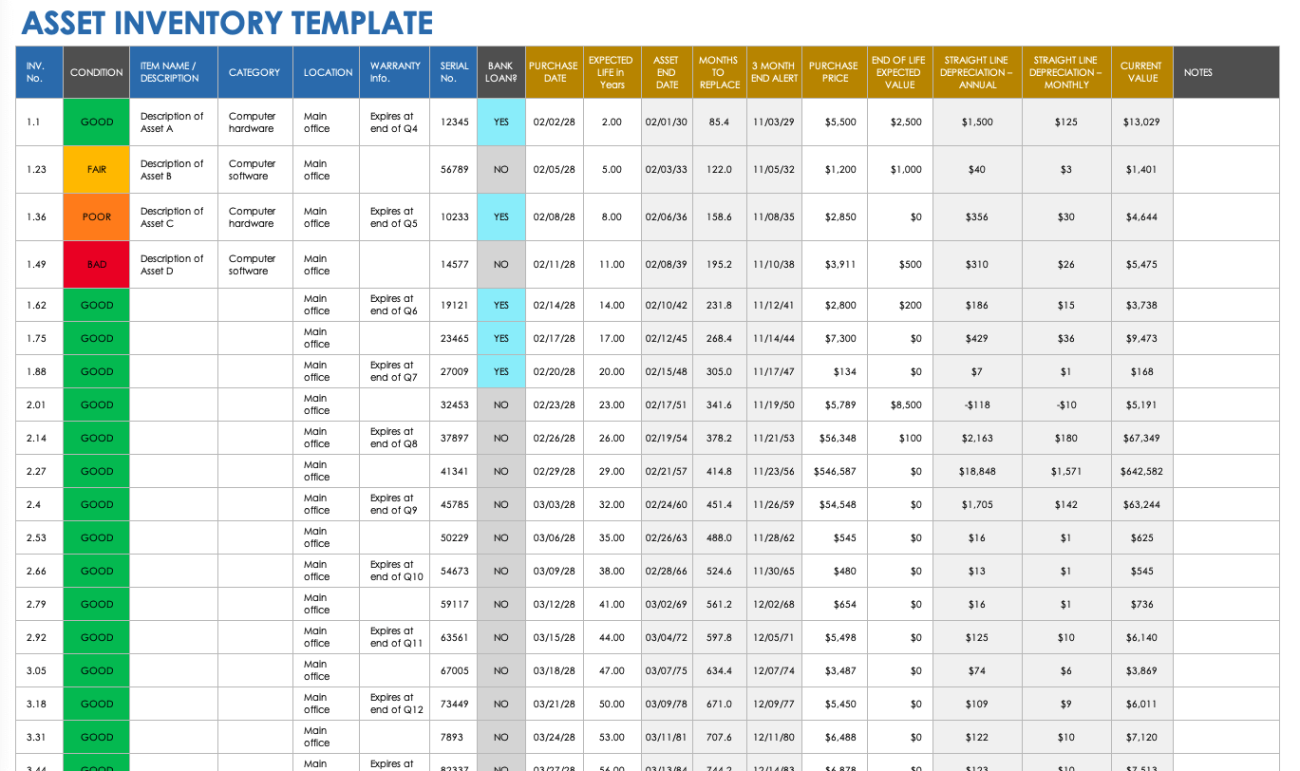
A business assets inventory is a comprehensive list of all the assets owned by a company. It includes both tangible and intangible assets, and it provides a detailed description of each asset, including its value and location.
The key components of a business assets inventory include:
- Asset name:The name of the asset, such as “computer” or “building.”
- Asset description:A brief description of the asset, including its make, model, and serial number.
- Asset value:The value of the asset, as determined by an appraisal or other valuation method.
- Asset location:The location of the asset, such as “office” or “warehouse.”
- Asset condition:The condition of the asset, such as “new” or “used.”
- Asset age:The age of the asset, such as “1 year” or “5 years.”
Tangible Assets
Tangible assets are physical assets that can be seen and touched. Examples of tangible assets include:
- Cash
- Accounts receivable
- Inventory
- Equipment
- Land
- Buildings
Intangible Assets
Intangible assets are non-physical assets that have value. Examples of intangible assets include:
- Goodwill
- Trademarks
- Patents
- Copyrights
- Data
- Customer relationships
Methods for Valuing Different Types of Assets, Are business assets inventory
The value of an asset can be determined using a variety of methods. The most common methods include:
- Appraisal:An appraisal is an estimate of the value of an asset by a qualified professional.
- Market value:The market value of an asset is the price that it would sell for in the open market.
- Book value:The book value of an asset is the value that it is recorded on the company’s financial statements.
- Replacement cost:The replacement cost of an asset is the cost of replacing it with a new asset of similar quality.
Uses of a Business Assets Inventory
A business assets inventory is a crucial tool for businesses of all sizes, providing a comprehensive overview of all the assets owned by the organization. This inventory serves various purposes, including financial reporting, asset management, decision-making, and strategic planning.
Financial reporting requires accurate information on the assets of a business. An inventory provides this information, enabling businesses to prepare financial statements that comply with accounting standards and regulations. These statements provide insights into the financial health of the business and are essential for stakeholders, including investors, creditors, and management.
Role in Asset Management and Decision-Making
Asset management involves the efficient and effective utilization of assets to achieve business objectives. A comprehensive inventory facilitates this process by providing a detailed record of all assets, including their location, condition, and value. This information enables businesses to make informed decisions regarding asset acquisition, disposal, and maintenance.
Decision-making in businesses often relies on accurate data about assets. An inventory provides this data, helping businesses assess the value of their assets, optimize resource allocation, and make informed investment decisions. For instance, a business may use an inventory to identify underutilized assets that can be sold or leased to generate additional revenue.
Strategic Planning
Strategic planning involves setting long-term goals and developing strategies to achieve them. A business assets inventory plays a vital role in this process by providing insights into the current state of the business’s assets and their potential impact on future plans.
By analyzing the inventory, businesses can identify opportunities for growth, assess risks, and develop strategies to enhance their overall performance.
- Example 1:A manufacturing company uses an inventory to identify obsolete equipment that can be replaced with more efficient models, improving productivity and reducing operating costs.
- Example 2:A retail business uses an inventory to determine the optimal level of inventory to maintain, minimizing the risk of stockouts while reducing storage costs.
Best Practices for Managing a Business Assets Inventory
Maintaining an accurate and up-to-date business assets inventory is crucial for efficient asset management. Here are some industry best practices to ensure effective inventory management:
Regular Audits and Reconciliation
Conducting regular audits of your business assets inventory is essential to ensure accuracy and prevent discrepancies. Audits should verify the physical existence of assets, compare inventory records with physical counts, and identify any discrepancies or missing items. Reconciliation involves matching inventory records with financial records to ensure that all assets are accounted for and valued correctly.
Implementing an Effective Inventory Management System
Invest in a robust inventory management system that streamlines asset tracking and provides real-time visibility into your inventory. This system should allow you to track asset location, usage history, maintenance schedules, and other relevant data. By automating inventory processes, you can improve accuracy, reduce manual errors, and enhance overall efficiency.
Case Studies and Examples
Many businesses have achieved success by effectively managing their asset inventories. Let’s explore some case studies and examples:
Caterpillar
Caterpillar, a leading manufacturer of heavy machinery, implemented a comprehensive asset inventory system that tracked every asset across its global operations. This system enabled Caterpillar to optimize asset utilization, reduce maintenance costs, and improve supply chain efficiency.
Nike
Nike, a sportswear giant, uses an advanced asset tracking system to manage its vast inventory of footwear, apparel, and accessories. This system provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, enabling Nike to respond quickly to changes in demand and minimize waste.
Challenges and Lessons Learned
While implementing and managing asset inventories can be beneficial, businesses often face challenges:
- Data accuracy:Ensuring the accuracy of asset data can be difficult, especially with large and complex inventories.
- Integration with other systems:Integrating asset inventory systems with other business systems, such as ERP and CRM, can be complex and time-consuming.
- Employee adoption:Encouraging employees to consistently use and update asset inventory systems can be challenging.
Lessons learned from these case studies include the importance of:
- Establishing clear asset management policies and procedures.
- Investing in technology and resources to support asset inventory management.
- Training employees on the importance and use of asset inventory systems.
Final Thoughts

Managing business assets inventory effectively requires a combination of best practices, regular audits, and a robust inventory management system. By implementing these measures, businesses can gain a competitive advantage, improve their financial performance, and mitigate risks associated with asset mismanagement.
Clarifying Questions: Are Business Assets Inventory
What is the purpose of a business assets inventory?
A business assets inventory provides a comprehensive list and description of all the assets owned by a company, helping businesses track their resources, assess their value, and make informed decisions about their use and allocation.
What are the key components of a business assets inventory?
Key components of a business assets inventory include tangible assets (e.g., equipment, inventory, land, buildings) and intangible assets (e.g., patents, trademarks, goodwill). Each asset should be described in detail, including its acquisition cost, depreciation schedule, and current value.
How is a business assets inventory used?
A business assets inventory is used for various purposes, including financial reporting, asset management, and strategic planning. It helps businesses track their assets, assess their value, make informed decisions about their use and allocation, and comply with regulatory requirements.
